03. 创建 Chirps
现在您已准备好开始构建您的新应用程序!让我们允许我们的用户发布称为Chirps的简短消息。
模型、迁移和控制器
为了允许用户发布 Chirps,我们需要创建模型、迁移和控制器。让我们更深入地探讨每个概念。
- 模型为您提供了一个强大且愉快的界面,用于与数据库中的表进行交互。
- 迁移允许您轻松创建和修改数据库中的表。它们确保您的应用程序在所有运行环境中都具有相同的数据库结构。
- 控制器 负责处理发送到应用程序的请求并返回响应。
几乎你构建的每个功能都将涉及所有这些部分协同工作,因此 artisan make:model 命令可以一次性为你创建所有这些部分。
让我们使用以下命令为我们的 Chirps 创建一个模型、迁移和资源控制器
php artisan make:model -mrc Chirp
你可以通过运行 php artisan make:model --help 命令查看所有可用选项。
此命令将为你创建三个文件
-
app/Models/Chirp.php- Eloquent 模型。 -
database/migrations/<timestamp>_create_chirps_table.php- 将创建你的数据库表的数据库迁移。 -
app/Http/Controllers/ChirpController.php- 将接收传入请求并返回响应的 HTTP 控制器。
路由
我们还需要为我们的控制器创建 URL。我们可以通过添加“路由”来实现,这些路由在项目的 routes 目录中管理。因为我们使用的是资源控制器,所以我们可以使用单个 Route::resource() 语句来定义所有遵循传统 URL 结构的路由。
首先,我们将启用两个路由
index路由将显示我们的表单和 Chirps 列表。store路由将用于保存新的 Chirps。
我们还将把这些路由放在两个 中间件 后面
auth中间件确保只有登录用户才能访问该路由。verified中间件将在你决定启用 电子邮件验证 时使用。
<?php +use App\Http\Controllers\ChirpController; use App\Http\Controllers\ProfileController; use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route; Route::get('/', function () { return view('welcome'); }); Route::get('/dashboard', function () { return view('dashboard'); })->middleware(['auth', 'verified'])->name('dashboard'); Route::middleware('auth')->group(function () { Route::get('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'edit'])->name('profile.edit'); Route::patch('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'update'])->name('profile.update'); Route::delete('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'destroy'])->name('profile.destroy'); }); +Route::resource('chirps', ChirpController::class)+ ->only(['index', 'store'])+ ->middleware(['auth', 'verified']); require __DIR__.'/auth.php';这将创建以下路由
| 动词 | URI | 操作 | 路由名称 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /chirps |
index | chirps.index |
| POST | /chirps |
store | chirps.store |

你可以通过运行 php artisan route:list 命令查看应用程序的所有路由。
让我们通过从新 ChirpController 类的 index 方法返回测试消息来测试我们的路由和控制器
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers; use App\Models\Chirp; use Illuminate\Http\Request; +use Illuminate\Http\Response; class ChirpController extends Controller { /** * Display a listing of the resource. */- public function index()+ public function index(): Response {- //+ return response('Hello, World!'); }
/** * Show the form for creating a new resource. */ public function create() { // } /** * Store a newly created resource in storage. */ public function store(Request $request) { // } /** * Display the specified resource. */ public function show(Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Show the form for editing the specified resource. */ public function edit(Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Update the specified resource in storage. */ public function update(Request $request, Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Remove the specified resource from storage. */ public function destroy(Chirp $chirp) { // } }如果你之前仍然登录,你应该在导航到 https://:8000/chirps 或 https:///chirps(如果你使用的是 Sail!)时看到你的消息。
Blade
还不够令人印象深刻?让我们更新 ChirpController 类的 index 方法以渲染 Blade 视图
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers; use App\Models\Chirp; use Illuminate\Http\Request; use Illuminate\Http\Response;+use Illuminate\View\View; class ChirpController extends Controller { /** * Display a listing of the resource. */- public function index(): Response+ public function index(): View {- return response('Hello, World!');+ return view('chirps.index'); }
/** * Show the form for creating a new resource. */ public function create() { // } /** * Store a newly created resource in storage. */ public function store(Request $request) { // } /** * Display the specified resource. */ public function show(Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Show the form for editing the specified resource. */ public function edit(Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Update the specified resource in storage. */ public function update(Request $request, Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Remove the specified resource from storage. */ public function destroy(Chirp $chirp) { // } }然后我们可以使用用于创建新的 Chirps 的表单来创建我们的 Blade 视图模板
<x-app-layout> <div class="max-w-2xl mx-auto p-4 sm:p-6 lg:p-8"> <form method="POST" action="{{ route('chirps.store') }}"> @csrf <textarea name="message" placeholder="{{ __('What\'s on your mind?') }}" class="block w-full border-gray-300 focus:border-indigo-300 focus:ring focus:ring-indigo-200 focus:ring-opacity-50 rounded-md shadow-sm" >{{ old('message') }}</textarea> <x-input-error :messages="$errors->get('message')" class="mt-2" /> <x-primary-button class="mt-4">{{ __('Chirp') }}</x-primary-button> </form> </div></x-app-layout>就是这样!刷新浏览器页面,您将看到 Breeze 提供的默认布局中呈现的新表单!
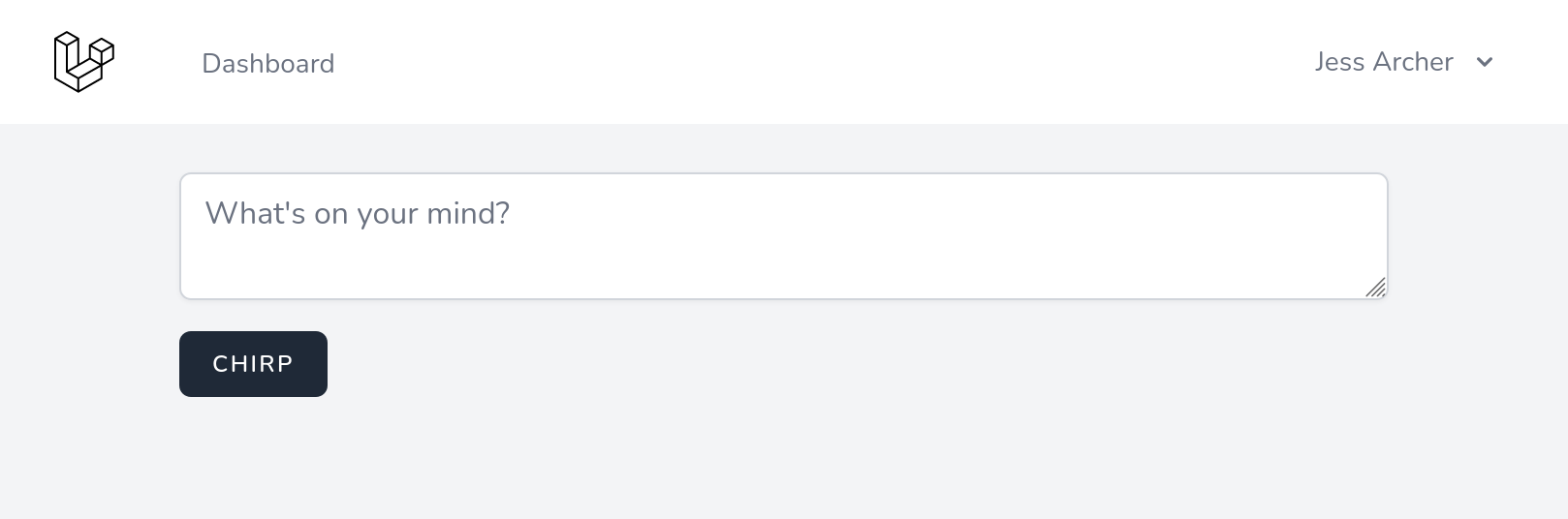
如果您的屏幕截图看起来与上面的不同,您可能需要停止并重新启动 Vite 开发服务器,以便 Tailwind 能够检测到我们刚刚创建的新文件中的 CSS 类。
从现在开始,我们对 Blade 模板所做的任何更改都将在 Vite 开发服务器运行时(通过 npm run dev)自动在浏览器中刷新。
导航菜单
让我们花点时间在 Breeze 提供的导航菜单中添加一个链接。
更新 Breeze 提供的 navigation.blade.php 组件,为桌面屏幕添加一个菜单项
<div class="hidden space-x-8 sm:-my-px sm:ml-10 sm:flex"> <x-nav-link :href="route('dashboard')" :active="request()->routeIs('dashboard')"> {{ __('Dashboard') }} </x-nav-link>+ <x-nav-link :href="route('chirps.index')" :active="request()->routeIs('chirps.index')">+ {{ __('Chirps') }}+ </x-nav-link> </div>以及移动屏幕
<div class="pt-2 pb-3 space-y-1"> <x-responsive-nav-link :href="route('dashboard')" :active="request()->routeIs('dashboard')"> {{ __('Dashboard') }} </x-responsive-nav-link>+ <x-responsive-nav-link :href="route('chirps.index')" :active="request()->routeIs('chirps.index')">+ {{ __('Chirps') }}+ </x-responsive-nav-link> </div>保存 Chirp
我们的表单已配置为将消息发布到我们之前创建的 chirps.store 路由。让我们更新 ChirpController 类中的 store 方法,以验证数据并创建一个新的 Chirp
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers; use App\Models\Chirp;+use Illuminate\Http\RedirectResponse; use Illuminate\Http\Request; use Illuminate\Http\Response; use Illuminate\View\View; class ChirpController extends Controller {
/** * Display a listing of the resource. */ public function index(): View { return view('chirps.index'); } /** * Show the form for creating a new resource. */ public function create() { // } /** * Store a newly created resource in storage. */- public function store(Request $request)+ public function store(Request $request): RedirectResponse {- //+ $validated = $request->validate([+ 'message' => 'required|string|max:255',+ ]);+ + $request->user()->chirps()->create($validated);+ + return redirect(route('chirps.index')); }
/** * Display the specified resource. */ public function show(Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Show the form for editing the specified resource. */ public function edit(Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Update the specified resource in storage. */ public function update(Request $request, Chirp $chirp) { // } /** * Remove the specified resource from storage. */ public function destroy(Chirp $chirp) { // } }我们使用 Laravel 强大的验证功能来确保用户提供消息,并且该消息不会超过我们将要创建的数据库列的 255 个字符限制。
然后,我们创建一个记录,该记录将属于登录用户,方法是利用 chirps 关系。我们很快就会定义这种关系。
最后,我们可以返回一个重定向响应,将用户发送回 chirps.index 路由。
创建关系
您可能在前面的步骤中注意到,我们在 $request->user() 对象上调用了 chirps 方法。我们需要在 User 模型上创建此方法,以定义一个 "一对多" 关系
<?php
namespace App\Models; // use Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\MustVerifyEmail; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;+use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\HasMany; use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable; use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable; use Laravel\Sanctum\HasApiTokens; class User extends Authenticatable {
use HasApiTokens, HasFactory, Notifiable; /** * The attributes that are mass assignable. * * @var array<int, string> */ protected $fillable = [ 'name', 'email', 'password', ]; /** * The attributes that should be hidden for serialization. * * @var array<int, string> */ protected $hidden = [ 'password', 'remember_token', ]; /** * Get the attributes that should be cast. * * @return array<string, string> */ protected function casts(): array { return [ 'email_verified_at' => 'datetime', 'password' => 'hashed', ]; } + public function chirps(): HasMany+ {+ return $this->hasMany(Chirp::class);+ } }
Laravel 提供了许多不同类型的模型关系,您可以在 Eloquent 关系 文档中了解更多信息。
批量赋值保护
将请求中的所有数据传递给模型存在风险。想象一下,您有一个页面供用户编辑其个人资料。如果您将整个请求传递给模型,那么用户可以编辑他们喜欢的任何列,例如is_admin列。这被称为批量赋值漏洞。
Laravel 默认阻止批量赋值,从而保护您免受意外操作的影响。但是,批量赋值非常方便,因为它可以防止您逐个分配每个属性。我们可以通过将安全属性标记为“可填充”来启用批量赋值。
让我们将$fillable属性添加到我们的Chirp模型中,以启用message属性的批量赋值。
<?php
namespace App\Models; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model; class Chirp extends Model {
use HasFactory; + protected $fillable = [+ 'message',+ ]; }您可以在文档中了解有关 Laravel 批量赋值保护的更多信息。
更新迁移
在应用程序创建期间,Laravel 已经应用了database/migrations目录中包含的默认迁移。您可以使用php artisan db:show和php artisan db:table命令检查当前数据库结构。
php artisan db:showphp artisan db:table users因此,唯一缺少的是数据库中的额外列,用于存储Chirp与其User之间的关系以及消息本身。还记得我们之前创建的数据库迁移吗?现在是打开该文件添加一些额外列的时候了。
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration; use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint; use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema; return new class extends Migration { /** * Run the migrations. */ public function up(): void { Schema::create('chirps', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id();+ $table->foreignId('user_id')->constrained()->cascadeOnDelete();+ $table->string('message'); $table->timestamps(); }); }
/** * Reverse the migrations. */ public function down(): void { Schema::dropIfExists('chirps'); } };我们还没有迁移数据库,因为我们添加了这个迁移,所以现在就来做吧。
php artisan migrate
每个数据库迁移只会执行一次。要对表进行其他更改,您需要创建另一个迁移。在开发过程中,您可能希望更新未部署的迁移并使用php artisan migrate:fresh命令从头开始重建数据库。
测试一下
我们现在可以使用刚刚创建的表单发送 Chirp 了!我们还无法看到结果,因为我们还没有在页面上显示现有的 Chirp。
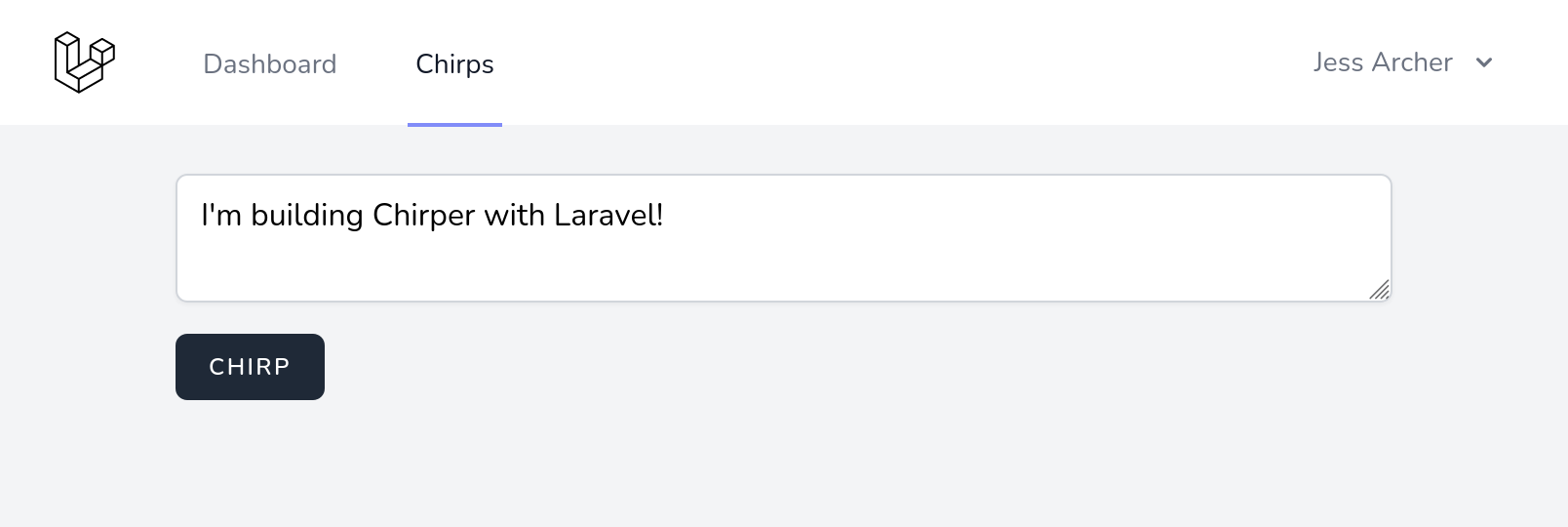
如果您将消息字段留空,或输入超过 255 个字符,那么您将看到验证生效。
Artisan Tinker
现在是学习Artisan Tinker的好时机,它是一个REPL (读-求值-打印循环),您可以在其中执行 Laravel 应用程序中的任意 PHP 代码。
在您的控制台中,启动一个新的 tinker 会话。
php artisan tinker接下来,执行以下代码以显示数据库中的 Chirps
App\Models\Chirp::all();=> Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection {#4512 all: [ App\Models\Chirp {#4514 id: 1, user_id: 1, message: "I'm building Chirper with Laravel!", created_at: "2022-08-24 13:37:00", updated_at: "2022-08-24 13:37:00", }, ], }您可以使用 `exit` 命令退出 Tinker,或按 Ctrl + c。
